./gradlew -Pprofile=gpp :htmlSanityCheck-gradle-plugin:login
Publishing HSC Releases
We distribute HSC for different usage scenarios to appropriate repositories, i.e., we publish
-
The HSC artifacts (Core, Maven plugin, and Gradle plugin) to Maven Central (MC) for retrieval by the common Java build tools,
-
The HSC Command Line Interface (CLI) distribution to
-
The HSC Gradle plugin additionally to Gradle Plugin Portal (GPP). GPP redirects to MC for any plugin (version) it cannot resolve. But without separate publication, the search index of GPP does not contain the plugin. Hence, retrieval of the plugin via the GPP Web UI would be impossible in this case.
Prerequisites
Maven Central (Sonatype) account
Make yourself familiar with the publishing process.
|
Maven Central credentials needed
You need respective credentials to upload files to Maven Central for the |
You will need to sign up for Maven Central (or, to be more precise, to its provider, Sonatype). Additionally, you need to create a portal token[1].
Check out JReleaser Credentials / Environment Settings how to inject these credentials in your environment for publication activities.
Gradle Plugin Portal
It is possible to publish new versions of the Plugin to the Gradle Plugin Portal.
|
Unique publisher required
Only one person at a time can take responsibility for publishing of plugins (Or new versions) to GPP. Currently, this is Gerd Aschemann (following Gernot Starke). Only the current maintainer can change the ownership (by creating a new ownership transformation request at https://github.com/gradle/plugin-portal-requests). |
After creating a user, you need to login to GPP:
This will put the respective key and secret to your ~/.gradle/gradle.properties file.
Alternatively, you can set these as environment variables:
export GRADLE_PUBLISH_KEY=...
export GRADLE_PUBLISH_SECRET=...SDKMAN
We registered HSC already as Vendor with SDKMAN. Publishing new releases requires API credentials (and authorization by an existing member of the HSC team, currently Gerd Aschemann).
We publish new versions to SDKMAN via the respective API, cf. JReleaser Credentials / Environment Settings.
Artifact signing
To successfully upload artifacts and other files (POM etc.), Maven Central requires a valid PGP signature.
A proper GPG (agent) setup is beyond the scope of this tutorial.
Therefore, you need to set up GnuPG in your local ${HOME}/.gradle/gradle.properties,
according to the Gradle Signatory documentation.
Add the following entries:
signing.keyId=24875D73 (1)
signing.secretKeyRingFile=/Users/me/.gnupg/secring.gpg (2)
signing.password=<SECRET> (3)| 1 | You have to provide the id of your key (of course). |
| 2 | Note that you need to specify the literal path to your home directory; it is not possible to refer to system properties like ${user.home} here. |
| 3 | Instead of putting the clear text password into the file, you should provide it on the command line when calling Gradle
|
|
Use GPG Agent
Alternatively, you may use the GPG Agent of your GnuPG installation to cache the secret in memory, thereby reducing the risk of accidentally exposing the clear text passphrase in your command line or environment. You can make use of it by setting the flag Note that the (native) In this case, you have to start the agent and cache the password, e.g., by executing |
JReleaser Credentials / Environment Settings
You will have to set the following environment variable to perform misc. JReleaser actions.
export JRELEASER_MAVENCENTRAL_STAGE=UPLOAD (1)
export JRELEASER_GITHUB_TOKEN=... (2)
export JRELEASER_DEPLOY_MAVEN_MAVENCENTRAL_USERNAME=... (3)
export JRELEASER_DEPLOY_MAVEN_MAVENCENTRAL_PASSWORD=... (3)
export JRELEASER_ANNOUNCE_MASTODON_ACCESS_TOKEN=... (4)
export JRELEASER_SDKMAN_CONSUMER_KEY=... (5)
export JRELEASER_SDKMAN_CONSUMER_TOKEN=... (5)| 1 | Maven Central publications require two steps. This variable setting enables upload to the staging area, perform the final publication interactively. |
| 2 | Get an appropriate GitHub token (needs write access to the repository). |
| 3 | Follow the steps above to get the required Maven credentials. Create a deployment user and password in your Maven Central (Sonatype) account. |
| 4 | Access token for your Mastodon Account (on https://mastodon.social[2]). |
| 5 | Key and Token for access to the SDKMAN API. |
Publishing actions
Adjust version number
Set the version number in ../../../gradle.properties to the next value.
Maintain ChangeLog
Add the respective changes to ../../../CHANGELOG.md
Build / Test
Clean, check (test), and perform integration tests:
./gradlew clean && ./gradlew check integrationTestPublish on Gradle Plugin Portal
Set the respective credentials (cf. GPP Prerequisites). Then publish on GPP:
./gradlew -Pprofile=gpp :htmlSanityCheck-gradle-plugin:publishPlugins (1)| 1 | An additional --validate-only allows to check credentials |
Performing this for the first time after a Change of the maintainer may take some time as the Gradle team will perform some checks.
|
You can delete the published version within 7 days if you fail with one of the following steps. Once published on Maven Central, you should not roll back this step. |
Sign / Stage to Maven Central and Publish to GitHub
Sign artifacts and load them up to Maven Central and GitHub via JReleaser.
./gradlew jreleaserRelease -PenableSigning=true -Psigning.password=... (1) (2)| 1 | Checkout Artifact signing for more information. |
| 2 | The enableSigning flag is necessary to enforce signing (which is not necessary for local installations,
integration testing, etc.) |
The jreleaserRelease task will perform several steps (all can be rolled back)
-
Implicitly call the task
signAllwhich signs and pushes all required files for publication to a local repository. -
Pick them up from there and load them up to the Maven Central staging area as a new version.
-
Release the current state to GitHub and tag the current version accordingly. This includes upload of ZIP- and TAR-application archives.
|
Use GPG Agent (command) in practice
If you have GPG configured properly, you may use the GPG-Agent. |
Publish to SDKMAN
./gradlew jreleaserPublishThis step makes the current version available via SDKMAN. However, as SDKMAN downloads the respective release from GitHub the publication to SDKMAN should follow the GitHub publication.
Publish on Maven Central (final step)
Eventually publish the staged version on Maven Central, i.e., Sonatype Central.
|
Once published, you cannot roll back the release on Maven Central as releases are immutable. Hence, run this step as the very last one if everything else ran smoothly. |
Publish documentation
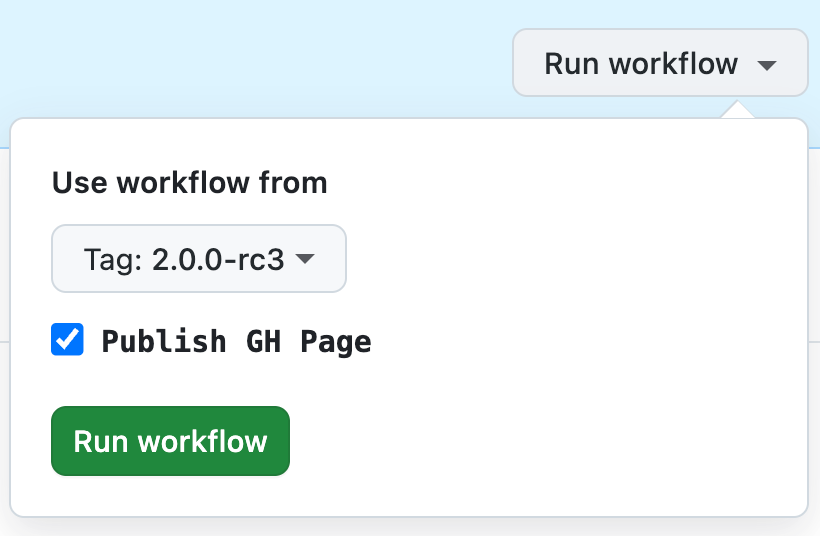
There is a GitHub Action Workflow to generate and publish the HSC documentation as GitHub page. Upon pushing Git commits of HSC, it builds the site and checks its integrity contents (by HSC itself), but does not publish it.
To finally publish the official documentation site, you have to trigger the workflow of the respective branch or tag with the checkmark Publish GH Page set.
Announce new release on Social Media
Finally, announce the new release on Social Media, i.e., Mastodon (Social).
./gradlew jreleaserAnnounceFeedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.